This patient was asymptomatic during the last follow up.
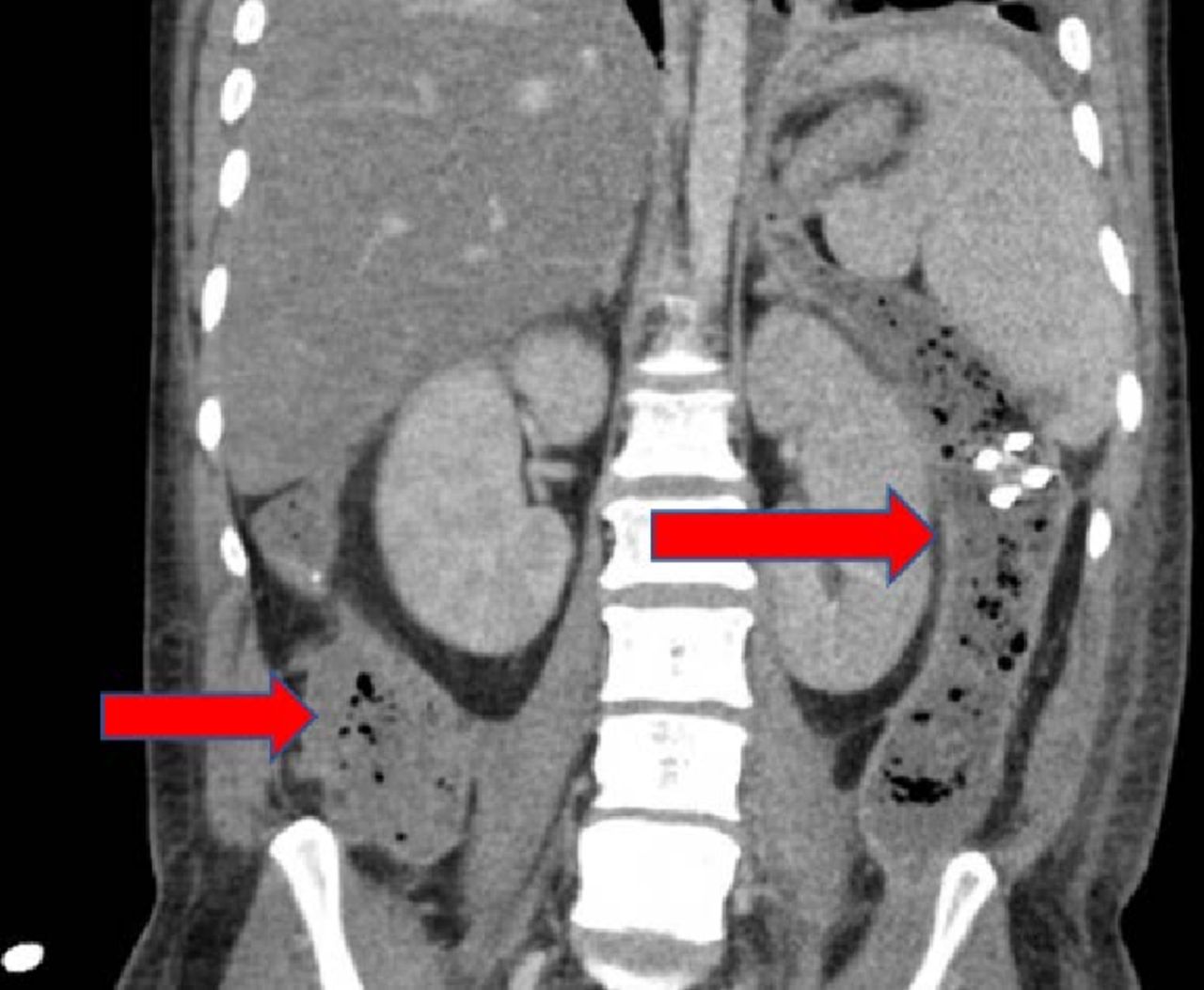
Pancreatic drainage into paracolic gutter.
Self expanding metal stents in the form of lumen apposing.
In a supine patient the peritoneal fluid tends to collect under the.
However peripancreatic collections that extend to the paracolic gutter or lesser sac are more challenging to treat endoscopically.
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
Walled off pancreatic necrosis won is a sequelae of acute pancreatitis that requires debridement once infected.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon.
When disruption of the pancreatic duct with leak was evident a pancreatic duct stent was placed using standard endoscopic techniques 25.
Two patients patients 8 and 12 developed recurrent pseudocysts after 2 and 4 months respectively.
The paracolic gutters slope into the subhepatic and subdiaphragmatic spaces superiorly and over the pelvic brim inferiorly.
When other peripancreatic collections expanded widely to paracolic.
Recently endoscopic necrosectomy has become the mainstay for management.
These collections are in close proximity to posterior wall of the stomach and thus amenable for internal drainage into the stomach.
The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon.
In cases where necrosis extends into one or both paracolic gutters and or into the pelvis the dependent portions of the collection will not be able to drain effectively through superiorly located transmural endoscopic.
The proximal tip of the pancreatic duct stent was advanced either well into the collection or bridged the site of pancreatic duct disruption.
Best practice advice 9.
The left medial paracolic gutter.
Both paracolic gutters run laterally along the back side of the abdominal wall and are situated between the abdominal wall and the outer margin of the colon.
Strongly considered as an adjunct to endoscopic drainage for won with deep extension into the paracolic gutters and pelvis or for salvage therapy after endoscopic or surgical debridement with residual necrosis burden.
Percutaneous drainage should be employed when endoscopic drainage is unavailable unsuccessful or not technically feasible.
Fluid collections developing from body and tail of pancreas form in the lesser sac.
Endoscopic therapy was combined with surgery because of necrosis extending into the paracolic gutter in patient 10.
Pfcs may also extend to left paracolic space.
Of necrotic collections that extend into the paracolic gutter.