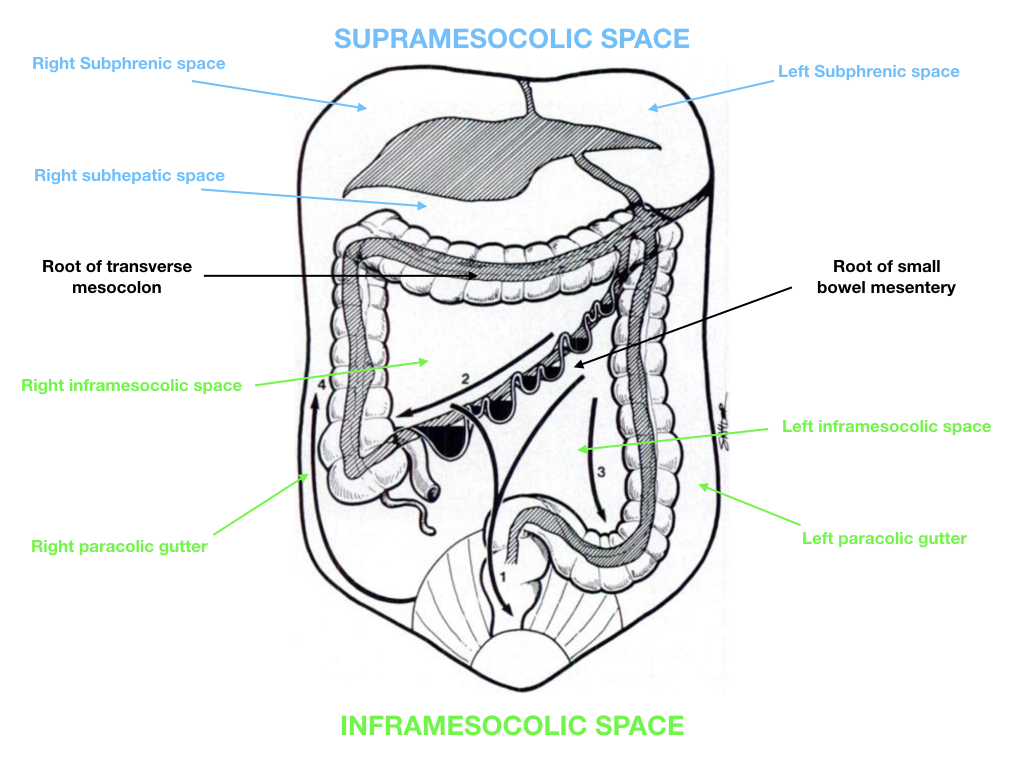
The right paracolic gutter is a component of the right inframesocolic space continuous superiorly with the right subhepatic and right subphrenic spaces it is larger than the left paracolic gutter which is partially separated from the left subphrenic spaces by the phrenicocolic ligament.
Paracolic gutter femoral vein.
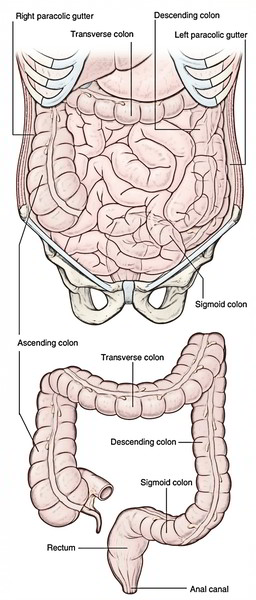
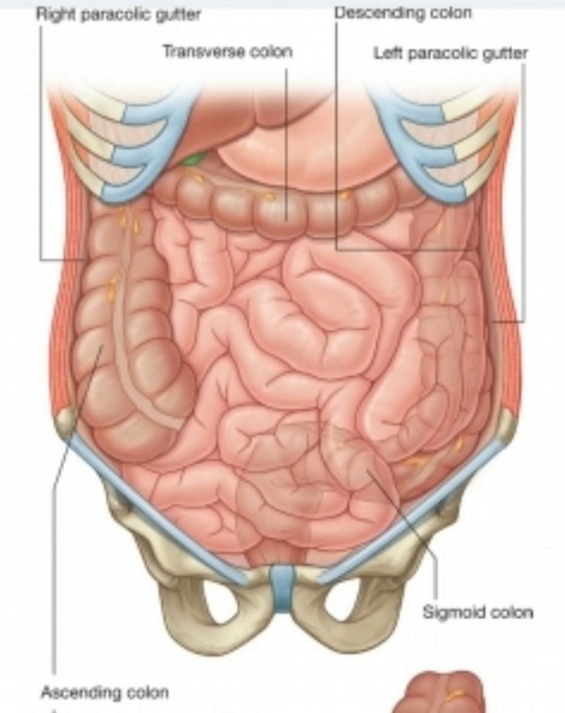
Its origin lies on the right side origin of the right paracolic gutter lies at the ascending portion of the colon at the right hepatic flexure or the point where the ascending colon turns at a right angle to form the transverse colon.
The left medial paracolic gutter.
However there is a wide differential for this pattern.
Hepatic artery proper portal vein bile duct.
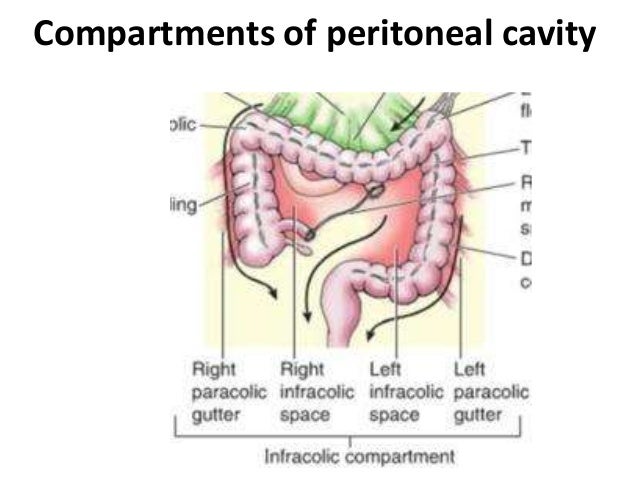
This allows the user to perfectly see the different parts of the peritoneal cavity omental bursa paracolic gutters mesentery mesocolon.
Gross anatomy origin posterior to inguinal ligament within lacuna vasorum 1 as continuation of femoral vein termination t.
The external iliac vein eiv is located along the pelvic brim between the inguinal ligament and the sacroiliac joint.
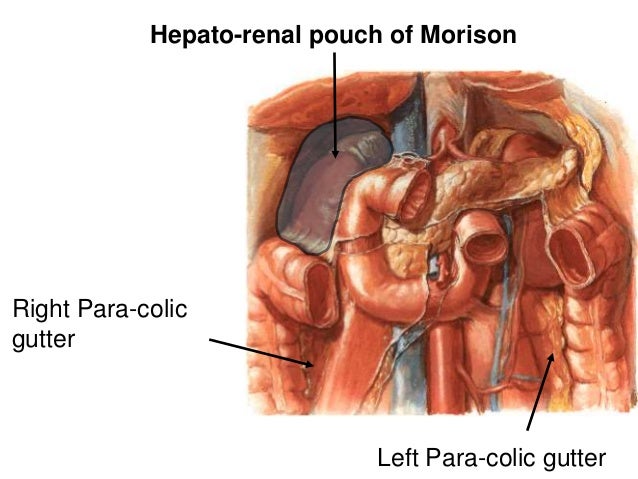
The right paracolic gutter is larger than the left and communicates freely with the right subphrenic space.
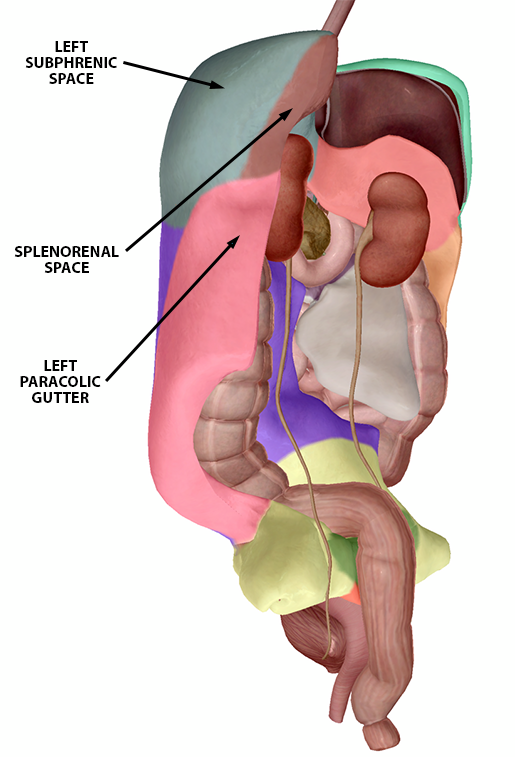
2 ruq view hepatorenal space subphrenic space right paracolic gutter liver tip right thoracic cavity 3 luq view splenorenal space subphrenic space left paracolic gutter left thoracic cavity 4 pelvic view longitudinal and transverse view of the bladder.
How may fluid get from the left paracolic gutter to the thorax.
It is smaller than the right paracolic gutter.
The paracolic spaces gutters are located lateral to the peritoneal reflections of the left and right sides of the colon fig 8a.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon.
The left paracolic gutter is a component of the left inframesocolic space partially separated from the left subphrenic spaces by the phrenicocolic ligament.
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
What makes up the portal triad.
The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon.
Due to back flow buildup in these veins creates this condition.
Both paracolic spaces are in continuity with the pelvic peritoneal spaces.
Portal to portal or portal to caval.
Both paracolic spaces are in continuity with the pelvic peritoneal spaces.
What vein connects the femoral vein with the axillary.